Cell–cell Interaction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cell–cell interaction refers to the direct interactions between
 Stable cell-cell interactions are required for
Stable cell-cell interactions are required for
cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
surfaces that play a crucial role in the development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development hell, when a project is stuck in development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
*Development (music), the process thematic material is reshaped
* Photograph ...
and function of multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- ...
organisms.
These interactions allow cells to communicate
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inquir ...
with each other in response to changes in their microenvironment. This ability to send and receive signals is essential for the survival of the cell. Interactions between cells can be stable such as those made through cell junctions
Cell junctions (or intercellular bridges) are a class of cellular structures consisting of multiprotein complexes that provide contact or adhesion between neighboring cells or between a cell and the extracellular matrix in animals. They also main ...
. These junctions are involved in the communication and organization of cells within a particular tissue. Others are transient or temporary such as those between cells of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
or the interactions involved in tissue inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
. These types of intercellular interactions are distinguished from other types such as those between cells and the extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide stru ...
. The loss of communication between cells can result in uncontrollable cell growth and cancer.
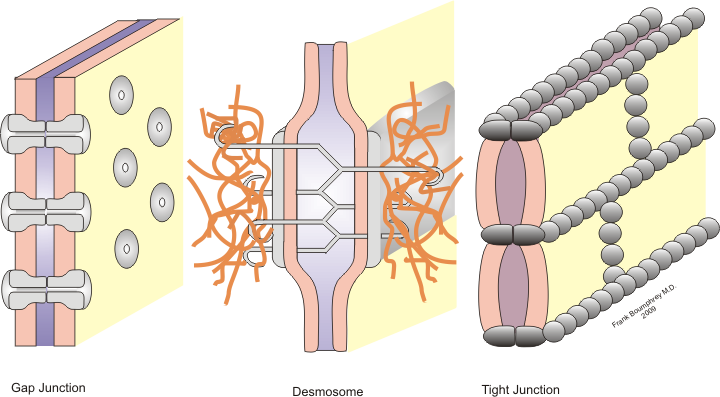
Stable interactions
 Stable cell-cell interactions are required for
Stable cell-cell interactions are required for cell adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as cell junctions or indir ...
within a tissue and controlling the shape and function of cells. These stable interactions involve cell junction
Cell junctions (or intercellular bridges) are a class of cellular structures consisting of multiprotein complexes that provide contact or adhesion between neighboring cells or between a cell and the extracellular matrix in animals. They also main ...
s which are multiprotein complexes that provide contact between neighboring cells. Cell junctions allow for the preservation and proper functioning of epithelial cell sheets. These junctions are also important in the organization of tissues where cells of one type can only adhere to cells of the same tissue rather than to a different tissue.
Tight junctions
Tight junction
Tight junctions, also known as occluding junctions or ''zonulae occludentes'' (singular, ''zonula occludens''), are multiprotein junctional complexes whose canonical function is to prevent leakage of solutes and water and seals between the epith ...
s are multi-protein complexes that hold cells of a same tissue together and prevent movement of water and water-soluble molecules between cells. In epithelial cells, they function also to separate the extracellular fluid surrounding their apical and basolateral membranes. These junctions exist as a continuous band located just below the apical
Apical means "pertaining to an apex". It may refer to:
*Apical ancestor, refers to the last common ancestor of an entire group, such as a species (biology) or a clan (anthropology)
*Apical (anatomy), an anatomical term of location for features loc ...
surface between the membranes of neighboring epithelial cells. The tight junctions on adjacent cells line up so as to produce a seal between different tissues and body cavities. For example, the apical surface of gastrointestinal epithelial cells serve as a selective permeable barrier that separates the external environment from the body. The permeability of these junctions is dependent on a variety of factors including protein makeup of that junction, tissue type and signaling
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' ...
from the cells.
Tight junctions are made up of many different proteins. The four main transmembrane proteins are occludin
Occludin is an enzyme ( EC 1.6) that oxidizes NADH. It was first identified in epithelial cells as a 65 kDa integral plasma-membrane protein localized at the tight junctions. Together with Claudins, and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), occludin has bee ...
, claudin
Claudins are a family of proteins which, along with occludin, are the most important components of the tight junctions ( zonulae occludentes). Tight junctions establish the paracellular barrier that controls the flow of molecules in the interce ...
, junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs) and tricellulins. The extracellular domains of these proteins form the tight junction barrier by making homophilic (between proteins of the same kind) and heterophilic interactions (between different types of proteins) with the protein domains on adjacent cells. Their cytoplasmic domains interact with the cell cytoskeleton to anchor them.
Anchoring junctions
Of the three types of anchoring junctions, only two are involved in cell-cell interactions:adherens junction
Adherens junctions (or zonula adherens, intermediate junction, or "belt desmosome") are protein complexes that occur at cell–cell junctions, cell–matrix junctions in epithelial and endothelial tissues, usually more basal than tight junctions. ...
s and desmosome
A desmosome (; "binding body"), also known as a macula adherens (plural: maculae adherentes) (Latin for ''adhering spot''), is a cell structure specialized for cell-to-cell adhesion. A type of junctional complex, they are localized spot-like adh ...
s. Both are found in many types of cells. Adjacent epithelial cells are connected by adherens junctions on their lateral membranes. They are located just below tight junctions. Their function is to give shape and tension to cells and tissues and they are also the site of cell-cell signaling. Adherens junctions are made of cell adhesion molecules from the cadherin
Cadherins (named for "calcium-dependent adhesion") are a type of cell adhesion molecule (CAM) that is important in the formation of adherens junctions to allow cells to adhere to each other . Cadherins are a class of type-1 transmembrane proteins, ...
family. There are over 100 types of cadherins, corresponding to the many different types of cells and tissues with varying anchoring needs. The most common are E-, N- and P-cadherins. In the adherens junctions of epithelial cells, E-cadherin
Cadherin-1 or Epithelial cadherin (E-cadherin), (not to be confused with the APC/C activator protein CDH1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CDH1'' gene. Mutations are correlated with gastric, breast, colorectal, thyroid, and ovarian ...
is the most abundant.
Desmosomes also provide strength and durability to cells and tissues and are located just below adherens junctions. They are sites of adhesion and do not encircle the cell. They are made of two specialized cadherins, desmoglein
The desmogleins are a family of desmosomal cadherins consisting of proteins DSG1, DSG2, DSG3, and DSG4. They play a role in the formation of desmosomes that join cells to one another.
Pathology
Desmogleins are targeted in the autoimmune disea ...
and desmocollin
Desmocollins are a subfamily of desmosomal cadherins, the transmembrane constituents of desmosomes. They are co-expressed with desmogleins to link adjacent cells by extracellular adhesion. There are seven desmosomal cadherins in humans, three des ...
. These proteins have extracellular domains that interact with each other on adjacent cells. On the cytoplasmic side, plakins form plaques which anchor the desmosomes to intermediate filaments composed of keratin proteins. Desmosomes also play a role in cell-cell signaling.
Gap junctions
Gap junctions
Gap junctions are specialized intercellular connections between a multitude of animal cell-types. They directly connect the cytoplasm of two cells, which allows various molecules, ions and electrical impulses to directly pass through a regulate ...
are the main site of cell-cell signaling or communication that allow small molecules to diffuse between adjacent cells. In vertebrates
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, ...
, gap junctions are composed of transmembrane proteins called connexin
Connexins (Cx)TC# 1.A.24, or gap junction proteins, are structurally related transmembrane proteins that assemble to form vertebrate gap junctions. An entirely different family of proteins, the innexins, form gap junctions in invertebrates. Ea ...
s. They form hexagonal pores or channels through which ions, sugars, and other small molecules can pass. Each pore is made of 12 connexin molecules; 6 form a hemichannel on one cell membrane and interact with a hemichannel on an adjacent cell membrane. The permeability of these junctions is regulated by many factors including pH and Ca2+ concentration.
Receptor proteins in direct-contact signaling
Receptor proteins on the cell surface have the ability to bind specific signaling molecules secreted by other cells.Cell signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellula ...
allows cells to communicate with adjacent cells, nearby cells (paracrine Paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse ove ...
) and even distant cells ( endocrine). This binding induces a conformational change in the receptor which, in turn, elicits a response in the corresponding cell. These responses include changes in gene expression and alterations in cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is compos ...
structure. The extracellular face of the plasma membrane has a variety of proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
, carbohydrates
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or may ...
, and lipids
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include ...
which project outward and act as signals. Direct contact between cells allows the receptors on one cell to bind the small molecules attached to the plasma membrane of different cell. In eukaryotes, many of the cells during early development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development hell, when a project is stuck in development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
*Development (music), the process thematic material is reshaped
* Photograph ...
communicate through direct contact.
Synaptic signaling, an integral part of nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes th ...
activity, occurs between neurons
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. N ...
and target cells. These target cells can also be neurons or other cell types (i.e. muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
or gland
In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream (endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface (exocrine gland).
Structure
De ...
cells). Protocadherin
Protocadherins (Pcdhs) are the largest mammalian subgroup of the cadherin superfamily of homophilic cell-adhesion proteins. They were discovered by Shintaro Suzuki's group, when they used PCR to find new members of the cadherin family. The PCR fr ...
s, a member of the cadherin
Cadherins (named for "calcium-dependent adhesion") are a type of cell adhesion molecule (CAM) that is important in the formation of adherens junctions to allow cells to adhere to each other . Cadherins are a class of type-1 transmembrane proteins, ...
family, mediate the adhesion of neurons to their target cells at synapses
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell.
Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses from ...
otherwise known as synaptic junctions. In order to for communication to occur between a neuron and its target cell, a wave of depolarization travels the length of the neuron and causes neurotransmitters
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neur ...
to be released into the synaptic junction. These neurotransmitters bind and activate receptors
Receptor may refer to:
*Sensory receptor, in physiology, any structure which, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds to a n ...
on the post-synaptic neuron thereby transmitting the signal to the target cell. Thus, a post-synaptic membrane belongs to the membrane receiving the signal, while a pre-synaptic membrane is the source of the neurotransmitter. In a neuromuscular junction
A neuromuscular junction (or myoneural junction) is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.
Muscles require innervation to ...
, a synapse is formed between a motor neuron
A motor neuron (or motoneuron or efferent neuron) is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectl ...
and muscle fibers
A muscle cell is also known as a myocyte when referring to either a cardiac muscle cell (cardiomyocyte), or a smooth muscle cell as these are both small cells. A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a muscl ...
. In vertebrates
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, ...
, acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Part ...
released from the motor neuron acts as a neurotransmitter which depolarizes the muscle fiber and causes muscle contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as ...
. A neuron’s ability to receive and integrate simultaneous signals from the environment and other neurons allows for complex animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
behavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as wel ...
.
Plant cell-cell interactions
Plant cells
Plant cells are the cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids with the capa ...
are surrounded by cell walls which are barriers for cell-cell communication. This barrier is overcome by specialized junctions called plasmodesmata
Plasmodesmata (singular: plasmodesma) are microscopic channels which traverse the cell walls of plant cells and some algal cells, enabling transport and communication between them. Plasmodesmata evolved independently in several lineages, and spec ...
. They are similar to gap junctions, connecting the cytosol of adjacent cells. Small molecules (<1000 Da), such as ions, amino acids, and sugars, can diffuse freely through plasmodesmata. These small molecules include signaling molecule
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a Cell (biology), cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property ...
and transcription factors
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The func ...
. The size of the channel is also regulated to allow molecules up to 10,000 Da in size. The permeability of these channels is dependent on many factors, including Ca2+ concentration. An increase in cytosolic Ca2+ concentration will reversibly limit passage through the plasmodesmata. Unlike gap junctions, the cell membranes of adjacent cells merge to form a continuous channel called an annulus. Additionally, within the channel, there is an extension of the endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ( ...
, called a desmotubule, which spans between the cells. The cell-cell interactions facilitated by plasmodesmata play an important role in development of plant cells and tissues and defense against viral infection.
Transient interactions
Immune system
Leukocytes
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
or white blood cells destroy abnormal cells and also provide protection against bacteria and other foreign matter. These interactions are transitory in nature but are crucial as an immediate immune response. To fight infection, leukocytes must move from the blood into the affected tissues. This movement into tissues is called extravasation
__NOTOC__
Extravasation is the leakage of a fluid out of its container into the surrounding area, especially blood or blood cells from vessels. In the case of inflammation, it refers to the movement of white blood cells from the capillaries to th ...
. It requires successive forming and breaking of cell-cell interactions between the leukocytes and the endothelial cells that line blood vessels. These cell-cell interactions are mediated mainly by a group of Cell Adhesion Molecules
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) are a subset of cell surface proteins that are involved in the binding of cells with other cells or with the extracellular matrix (ECM), in a process called cell adhesion. In essence, CAMs help cells stick to each ...
(CAMs) called selectins.
T helper cells
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considere ...
, central to the immune system, interact with other leukocytes by releasing signals known as cytokines
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
which activate and stimulate the proliferation of B cells
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or ...
and killer T cells
A cytotoxic T cell (also known as TC, cytotoxic T lymphocyte, CTL, T-killer cell, cytolytic T cell, CD8+ T-cell or killer T cell) is a T lymphocyte (a type of white blood cell) that kills cancer cells, cells that are infected by intracellular pa ...
. T helper cells also directly interact with macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
, cells that engulf foreign matter and display antigens
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. ...
on its surface. T-helper cells that possess the appropriate receptors can bind to these antigens and proliferate resulting in T-helper cells that have the ability to identify the same antigens.
Coagulation
Coagulation
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism o ...
or blood clotting relies on, in addition to the production of fibrin
Fibrin (also called Factor Ia) is a fibrous, non-globular protein involved in the clotting of blood. It is formed by the action of the protease thrombin on fibrinogen, which causes it to polymerize. The polymerized fibrin, together with platele ...
, interactions between platelets
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby ini ...
. When the endothelium
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel ...
or the lining of a blood vessel is damaged, connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
including collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole ...
fibers is locally exposed. Initially, platelets stick to the exposed connective tissue through specific cell-surface receptors. This is followed by platelet activation and aggregation in which platelets become firmly attached and release chemicals that recruit neighboring platelets to the site of vascular injury. A meshwork of fibrin then forms around this aggregation of platelets to increase the strength of the clot.
Cell interactions between bacteria
Bacterial populations interact in a similar manner to cells in tissue. They communicate through physical interactions and signaling molecules such as homoserine lactones and peptides as a means to control metabolism and regulate growth . A common example and one of the most studied forms of bacterial cell interactions is biofilm.Biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular ...
is a cell aggregate that can be attached to biological or abiotic surfaces. Bacteria form biofilms to adapt to various environments such as changes in substrate availability. For example, the formation of biofilm increases a bacterial cell's resistance to antibiotics compared to cells which are not part of the aggregate.
Pathological implications
Cancer
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
can result from the loss of cell-cell interaction. In normal cells, growth is controlled by contact inhibition In cell biology, contact inhibition refers to two different but closely related phenomena: contact inhibition of locomotion (CIL) and contact inhibition of proliferation (CIP). CIL refers to the avoidance behavior exhibited by fibroblast-like cells ...
in which contact with neighboring cells causes a stunt in cell growth. Contact inhibition is thought to be mediated by cadherin
Cadherins (named for "calcium-dependent adhesion") are a type of cell adhesion molecule (CAM) that is important in the formation of adherens junctions to allow cells to adhere to each other . Cadherins are a class of type-1 transmembrane proteins, ...
s, proteins that play an important role in cell adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as cell junctions or indir ...
. This inhibition prevents cells from piling up on top of one another and forming mounds. However, in cancerous cells where expression of E-cadherin is lost, contact inhibition is lost and results in uncontrolled growth or proliferation, tumor formation, and metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, ...
.
Bacterial pathogens
In order forpathogenic bacteria
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often Probiotic, beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The n ...
to invade a cell, communication with the host cell is required. The first step for invading bacteria is usually adhesion to host cells. Strong anchoring, a characteristic that determines virulence
Virulence is a pathogen's or microorganism's ability to cause damage to a host.
In most, especially in animal systems, virulence refers to the degree of damage caused by a microbe to its host. The pathogenicity of an organism—its ability to ca ...
, prevents the bacteria from being washed away before infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
occurs. Bacterial cells can bind to many host cell surface structures such as glycolipids and glycoproteins which serve as attachment receptors. Once attached, the bacteria begin to interact with the host to disrupt its normal functioning and disrupt or rearrange its cytoskeleton. Proteins on the bacteria surface can interact with protein receptors on the host thereby affecting signal transduction within the cell. Alterations to signaling are favorable to bacteria because these alterations provide conditions under which the pathogen can invade. Many pathogens have Type III secretion systems which can directly inject protein toxins
A toxin is a naturally occurring organic poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. Toxins occur especially as a protein or conjugated protein. The term toxin was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1 ...
into the host cells. These toxins ultimately lead to rearrangement of the cytoskeleton and entry of the bacteria.
Disease
Cell–cell interactions are highly specific and are tightly regulated. Genetic defects and dysregulation of these interactions can cause many different diseases. Dysregulation that leads to leukocyte migration into healthy tissues can cause conditions such asacute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin colo ...
and some types of arthritis
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In som ...
. The autoimmune disease pemphigus vulgaris results from autoantibodies to desmoglein
The desmogleins are a family of desmosomal cadherins consisting of proteins DSG1, DSG2, DSG3, and DSG4. They play a role in the formation of desmosomes that join cells to one another.
Pathology
Desmogleins are targeted in the autoimmune disea ...
and other normal body proteins. The autoantibodies disrupt the adhesion between epithelial cells. This causes blisters of the skin and mucous membranes. Mutations in the connexin genes cause 8 human diseases including heart malformations and neurosensory deafness.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cell-cell interaction Cell biology Cell communication Cell signaling Molecular biology